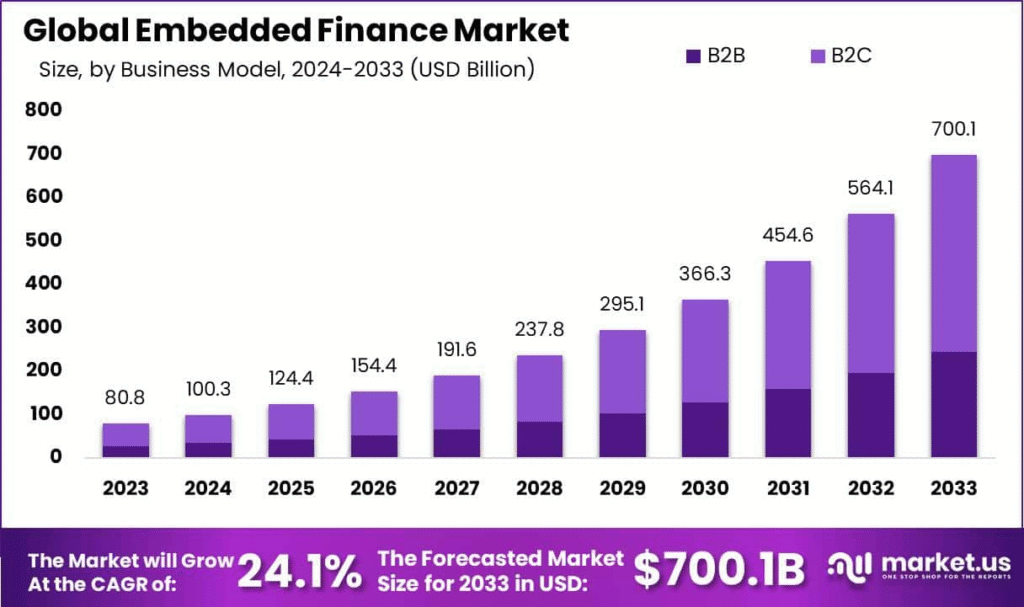
Embedded finance is revolutionizing how financial services are delivered and consumed worldwide, including Pakistan. By seamlessly integrating financial products such as payments, lending, and insurance into non-financial platforms and everyday business processes, embedded finance is transforming the Pakistani business landscape, particularly for SMEs and startups.
Defining Embedded Finance
Embedded finance refers to the integration of financial services directly into the platforms of non-financial businesses. Rather than customers interacting with banks or financial institutions separately, these financial products are embedded within apps, websites, or services they already use—allowing instant access to payment, credit, insurance, or investment options at the point of need.
This integration is typically enabled by APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and fintech innovations, making transactions seamless, faster, and more intuitive. Embedded finance minimizes friction in financial interactions, often appearing during checkout processes or service engagements without requiring customers to visit a bank or open separate accounts.
Types of Embedded Financial Products
Embedded finance encompasses a wide range of products, including but not limited to:
- Embedded Payments: Allowing instant payments or checkouts within apps or e-commerce platforms.
- Embedded Lending: Offering instant credit or loans integrated into purchase processes (e.g., Buy Now Pay Later).
- Embedded Insurance: Insurance products offered directly through retail or service platforms.
- Embedded Banking Services: Accounts, cards, or wallets embedded into platforms, enabling users to manage finances without leaving the service ecosystem.
- Embedded Investment Services: Simplified investment options integrated into non-financial apps.
By embedding these services, companies can deliver a holistic customer experience while gaining new revenue streams.
Key Examples of Embedded Finance in Pakistan
Pakistan’s evolving fintech ecosystem is witnessing rapid growth in embedded finance models, with several practical applications:
1. Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL)
BNPL services are increasingly popular in Pakistan’s retail and e-commerce platforms, allowing consumers to instantly finance purchases with no upfront payment and pay over time in installments. This service is embedded at checkout points, making credit accessible without visiting banks.
2. Embedded Lending for SMEs and Startups
Fintech platforms and digital wallets are integrating lending APIs that assess a business’s transaction history and creditworthiness to offer instant loans. This embedded lending reduces paperwork and speeds up financing for small enterprises that traditionally faced barriers in accessing credit. Examples include partnered lending solutions integrated into business payment apps or e-commerce platforms.
3. Payments in Ride-Hailing and Delivery Apps
Ride-hailing services like Careem and delivery platforms have embedded digital payments allowing seamless fare collection, driver payouts, or in-app wallet top-ups without requiring users to interact with third-party banks explicitly.
4. Embedded Wallets and Banking
Some platforms offer embedded wallets or account services within their apps, enabling peer-to-peer transfers, bill payments, and other banking features directly within the platform. These digital-first experiences enhance convenience and foster loyalty.
Impact on SMEs and Startups
Embedded finance is particularly transformative for Pakistani SMEs and startups by:
- Simplifying Access to Finance: Embedded lending reduces traditional barriers such as collateral demands and lengthy approvals.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Embedded payment options in platforms improve transaction speed and convenience, increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
- Enabling Growth: Easier financing and integrated payments help businesses scale faster and enter digital marketplaces.
- Formalizing the Economy: Embedded finance encourages informal businesses to adopt digital payments and finance tools, increasing transparency and enabling better financial management.
Benefits of Embedded Finance
- Simplicity: Financial services are delivered at the point of need, eliminating unnecessary steps.
- Speed: Instant approvals and seamless transactions save time.
- Improved Customer Experience: Embedded products reduce friction, leading to higher customer retention and satisfaction.
- New Revenue Streams for Businesses: Non-financial firms earn fees and increase engagement.
- Greater Financial Inclusion: Especially for unbanked or underbanked populations accessing financial services through familiar digital channels.
Challenges: Regulation and Data Privacy
While promising, embedded finance also brings challenges:
- Regulatory Compliance: Financial services must comply with stringent regulations by the State Bank of Pakistan, including anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) rules. Ensuring fintechs and non-financial firms align with these can be complex.
- Data Privacy and Security: Embedding financial services requires handling sensitive personal and financial data. Protecting this data from breaches and misuse is critical to maintaining trust.
- Customer Awareness: Educating users about embedded finance benefits and risks is necessary to foster adoption.
- Integration Complexity: Technical and operational integration between financial providers and platforms can be demanding.
Overcoming these challenges will require a coordinated effort among regulators, fintech companies, and platform providers.
The Future of Embedded Finance: Trends and Innovation
Embedded finance is expected to grow substantially in Pakistan and globally, driven by:
- Increased API Use: APIs will enable more seamless integration of financial products across platforms.
- AI and Data Analytics: Personalized financial offers and risk assessment will improve credit access and customer targeting.
- Expansion of Buy Now Pay Later and Micro-lending: Flexible credit options tailored for consumers and SMEs.
- Banking-as-a-Service Models: Banks providing backend infrastructure to fintechs for embedded finance offerings.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Blockchain for secure transactions, and cryptocurrencies might offer new embedded payment methods.
- Greater Collaboration: Fintechs and traditional banks working together to provide innovative, scalable embedded financial solutions tailored for the Pakistani market.
Embedded finance is reshaping Pakistan’s business ecosystem by making financial services more accessible, convenient, and integrated into daily commerce and enterprise operations. For Pakistani SMEs and startups, this evolution offers a critical competitive edge and paths to financial empowerment.